The Role of Diffusion in Everyday Life: From Breathing to Cooking
Diffusion is a fundamental process that occurs in many areas of everyday life and plays a vital role in both biological and physical phenomena. It can be defined as the movement of molecules or particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration until equilibrium is reached. This passive transport mechanism does not require energy and is essential for numerous functions within living organisms as well as in everyday activities such as cooking.
Diffusion in Respiration
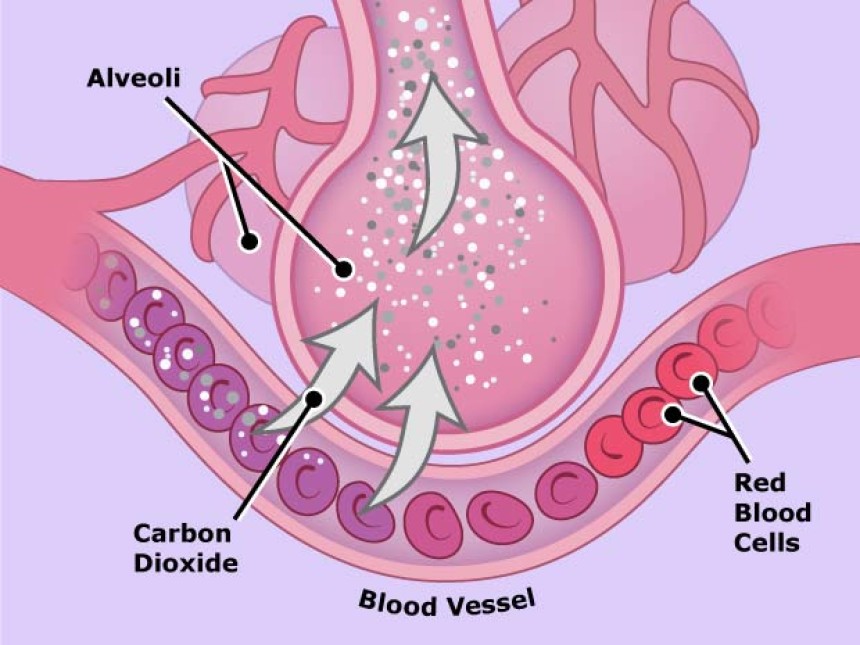
Respiration is one of the most important roles of diffusion. When we breathe, oxygen enters our lungs. The concentration of oxygen is higher than in the oxygen-poor blood in the capillaries surrounding the alveoli. The highly concentrated oxygen molecules enter the bloodstream from the alveolar region through diffusion, where they are transported by red blood cells to tissues throughout the body.
Diffusion in Digestion
In addition to respiration, diffusion also plays a vital role in digestion. When food is broken down in the digestive system, nutrients such as glucose enter the bloodstream through diffusion.
Diffusion During Cooking
When meat or vegetables are marinated, flavors are created through diffusion as molecules move from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration.
Diffusion in Food Preservation
Another practical application of diffusion is in food preservation techniques such as osmotic dehydration.
-I Love Biology Class- 😊





