There was an explosion on the motorbike you were using?
In a motorbike engine, an explosion occurs every time we use it, isn't that dangerous?
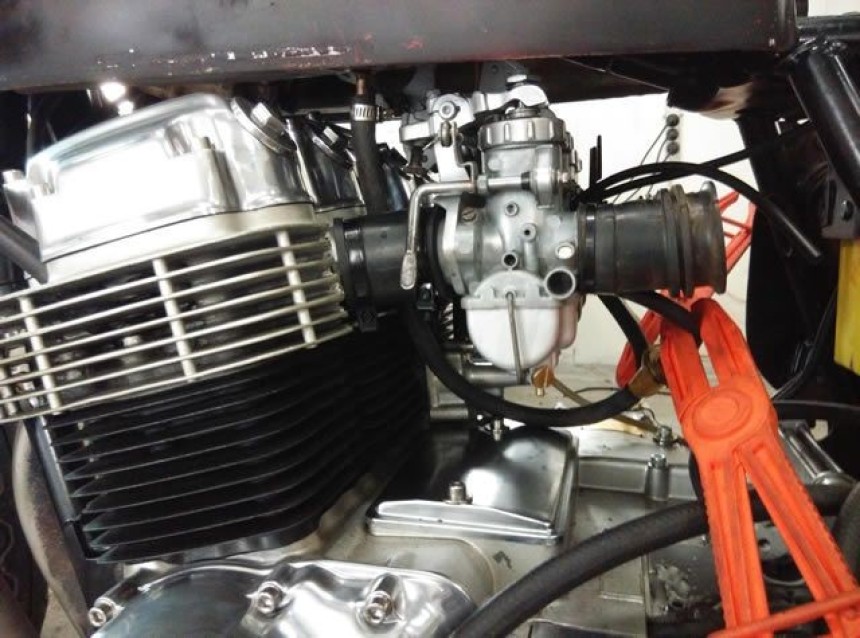
The explosion that occurred was one of the combustion processes in the motorbike engine. To be more precise, this takes place inside the combustion chamber. This process is the main process in the motorbike engine working system. Yes, this is what makes your motorbike move.
One part of a motorbike is called a spark plug. When it receives high pressure from the Ignition Coil, the spark plug emits sparks. This causes a spark and high temperature between the center electrode and the spark plug mass so that the compressed air and fuel mixture ignite. Despite experiencing high temperatures and pressure changes, spark plugs must be able to maintain the ability to ignite for a long period.
The mixture of air and fuel that the spark plug ignites to compress is what causes the explosion to occur. Based on their working principle, petrol motorbikes are divided into two types, namely, 2-stroke and 4-stroke petrol motors. We often call them 2-stroke or 4-stroke motorbikes.
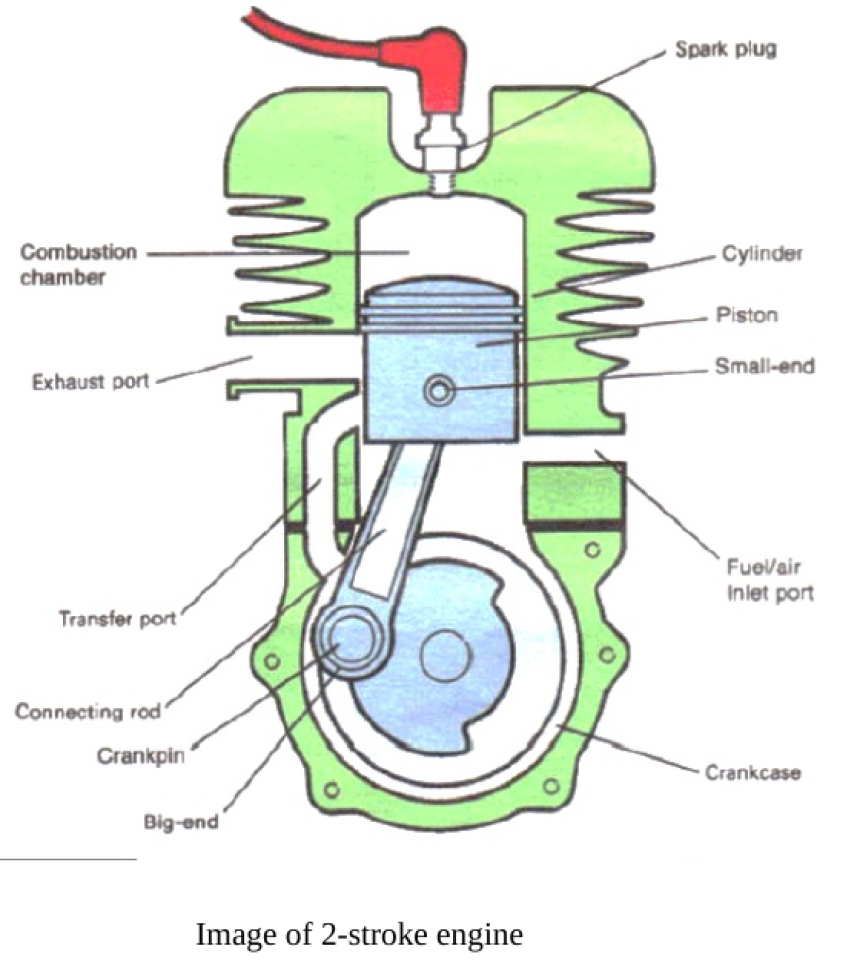
The working principle of a 2-stroke petrol motor consists of:
1. Suction and compression stroke:
- Piston moves up.
- The air and fuel mixture can enter the space under the piston because the space under the piston becomes empty or vacuum.
- The temperature and pressure of the air and fuel mixture in the upper chamber of the piston increase, caused by the compression stroke.
2. Business and waste steps:
- About 15 degrees before the piston reaches TDC (Top Dead Centre), the spark plug sparks, so that the combustion process takes place.
- This explosion causes the piston to be pushed back to BDC (Bottom Dead Centre), and the space under the piston becomes compressed.
- So that the air and fuel mixture in the space below the piston is pushed out and rises to the space above the piston through the rinse channel and is pushed by combustion gases from the cylinder out into the exhaust pipe.
This work step occurs repeatedly as long as the engine is running.
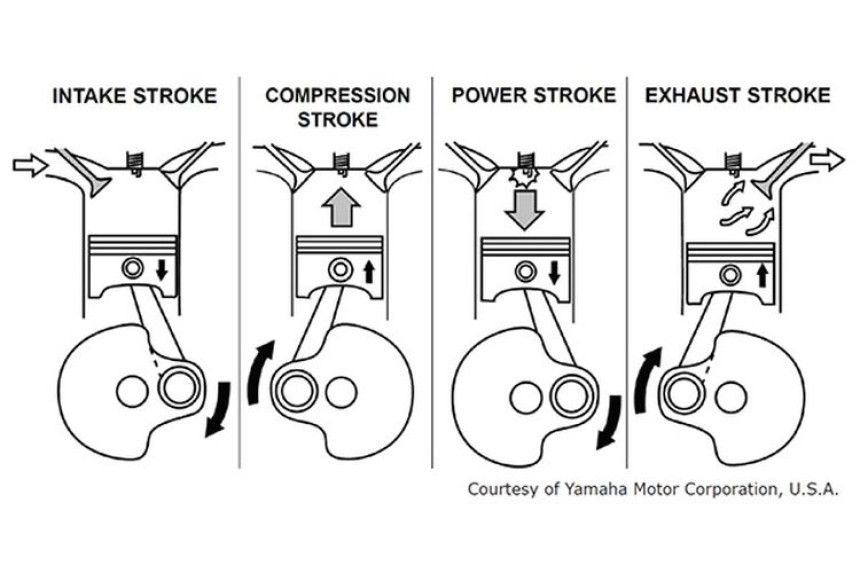
Just like the name implies, a 4-stroke engine is an engine that has 4 steps in one combustion cycle, with the following details:
1) Suction Steps (Intake):
The piston moves from Top Dead Center (TDC) to Bottom Dead Center (BDC), at the same time as the intake valve opens. Makes fuel enter the cylinder.
2) Compression Steps (Compression):
When the piston is at BDC, the intake and exhaust valves are closed. Then, the piston moves to TDC, the fuel is compressed in the combustion chamber. About 15 degrees before the piston reaches TDC, the spark plug sparks, so that the combustion process takes place. To increase the temperature, so that the mixture of fuel and air can be ignited. Where the ratio is, affects the power produced.
3) Power Steps:
The ignited mixture will propagate and cause an explosion that is contained by the cylinder. This explosion causes the piston to be pushed back to BDC. This movement is used as rotational motion by the crankshaft which is transmitted as momentum to the flywheel which produces power and carries out the next cycle.
4) Exhaust Steps:
The piston moves back to TDC, which then pushes the remaining combustion gases from the cylinder out into the exhaust pipe.
These steps keep repeating so that the motor can move.
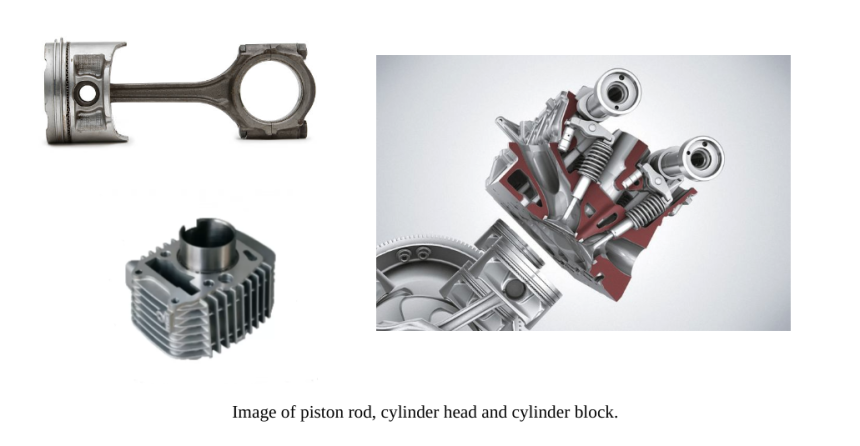
The components that make up the combustion chamber are the piston, cylinder block and cylinder head. So, the piston must be light, resistant to explosion pressure and resistant to expansion. The cylinder head is made of cast iron or aluminium alloy so it can withstand heat. Meanwhile, the cylinder block must be stiff, light and strong, have a construction that allows even cooling, and have good sliding properties (wear resistance).

That way, the explosion that occurs inside the machine is not dangerous. The existing components have been well designed according to their needs to carry out their respective functions. However, we still need to care for it and use it well so that the machine can function as it should. Don't forget to service your motorbike according to the schedule to avoid unwanted things happen.





